Check your Egress Filtering with a PowerShell port scan script

This is just a quick post so I can refer to myself more than anything regarding conducting a Powershell Port Scan! However this is a useful couple of lines to to conduct a port scan from a windows device with PowerShell. This can be used in a number of situations however is especially ideal to check your egress filtering out to a server on the internet or to a segmented network. In the below few lines we are testing the first 1000 ports this can be bumped up to 65535 if wanted and the server that you are port scanning is listed as X.X.X.X.
1..1000 | % {$test= new-object system.Net.Sockets.TcpClient;
$wait = $test.beginConnect("X.X.X.X",$_,$null,$null);
($wait.asyncwaithandle.waitone(50,$false)); if($test.Connected)
{echo "$_ open"}else{echo "$_ closed"}} | select-string " "
This particular script has been pulled from Black Hills Information Security page here. An alternative from Microsoft’s ‘Hey, Scripting Guy! Blog’ can be found here.
The Common Problem
Often organisations lack adequate egress filtering, by this I mean outbound connects that can be established on a number of ports from within the heart of the network. Client machines and typical internal application servers don’t need to access a range of services out on the Internet. Once a nasty exploit has got an attacker onto a network they will look to get a foothold within the network lateral move and phone home to command and control server. Having a range of ports open to clients and servers allows attackers to make an outbound connects from whole host of tools, including PowerShell for that matter.
The Solution
Check you egress filtering and lock down any unwanted open ports out to the internet, your perimeter firewalls should not allow these outbound connections. Obviously certain services are going to need to make outbound connections such as web proxy and email gateways and these rules should be appropriately provisioned. To take this one step further enable your outbound firewall rules on your local hosts, ‘hang on a sec, you must be crazy’ I hear you say, however by doing this you will be help prevent the lateral movement of attackers through your network as well as being able to get off your network back out to the Internet.


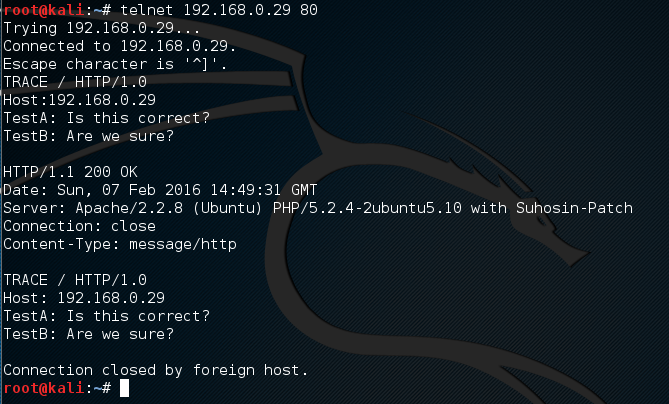
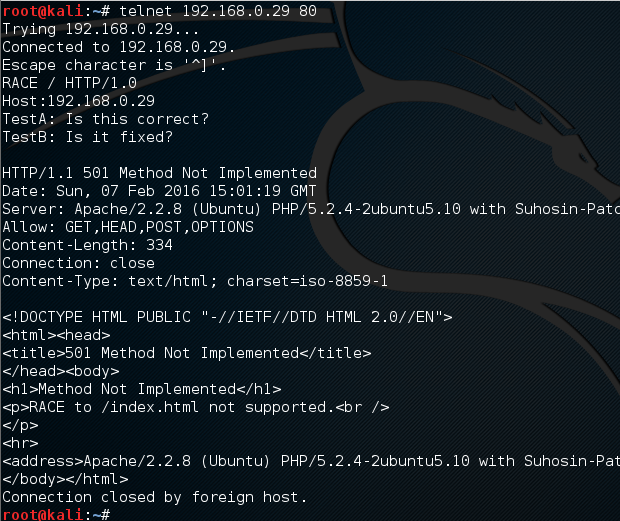
 Many vulnerability scanners will often bring back HTTP TRACE TRACK Methods Allowed against Apache and Microsoft web servers of the older generation. TRACE is usually associated with Apache and TRACK for Microsoft. This has a CVSS score of 4.3 and is a relatively easy fix. Clearly the older generation operating systems should be migrated to a supported platform, both the later distributions of Ubuntu and Microsoft 2012 R2 do not allow these methods to be used. However a simple way to validate this finding is to use telnet to connect to the web server on port 80, once connected you can type something similar to the following for each method. The ‘Host’, ‘TestA’ and ‘TestB’ aren’t needed however if you use some custom text you will be sure to see it echoed back by the web server if trace is enabled.
Many vulnerability scanners will often bring back HTTP TRACE TRACK Methods Allowed against Apache and Microsoft web servers of the older generation. TRACE is usually associated with Apache and TRACK for Microsoft. This has a CVSS score of 4.3 and is a relatively easy fix. Clearly the older generation operating systems should be migrated to a supported platform, both the later distributions of Ubuntu and Microsoft 2012 R2 do not allow these methods to be used. However a simple way to validate this finding is to use telnet to connect to the web server on port 80, once connected you can type something similar to the following for each method. The ‘Host’, ‘TestA’ and ‘TestB’ aren’t needed however if you use some custom text you will be sure to see it echoed back by the web server if trace is enabled.